Table of Contents
In linguistics and literacy studies, terms like grapheme, phoneme, and allograph are frequently used. Among these, the grapheme is central: it represents the smallest unit of written language, capable of conveying sounds, syllables, or even entire concepts.
Understanding graphemes is important not only for linguists but also for teachers, students, writers, and anyone studying the mechanics of language. In this guide, we will cover:
- What a grapheme is and its key characteristics
- The main types of graphemes: alphabetic, syllabic, and logographic
- The difference between grapheme and phoneme
- The difference between grapheme and allograph
- Practical examples in English
- Frequently asked questions (FAQ) for clarity
What is a Grapheme?
A grapheme is the smallest unit of written language, a symbol or combination of symbols representing a linguistic unit. Put simply, it is what allows the sounds and concepts of spoken language to be represented visually.
Key Characteristics of Graphemes
- Abstract: A grapheme represents a concept, not just a visual letter.
- Represents a phoneme or linguistic unit: It can indicate a single sound, a syllable, or occasionally a concept.
- Has graphic variants (allographs): Uppercase, lowercase, italic, or different fonts do not change the underlying grapheme.
- Present in various writing systems: Alphabetic, syllabic, and logographic.
Example: The letter a is a grapheme; it can appear as a, A, or in cursive a, but the concept of the “grapheme a” remains unchanged.

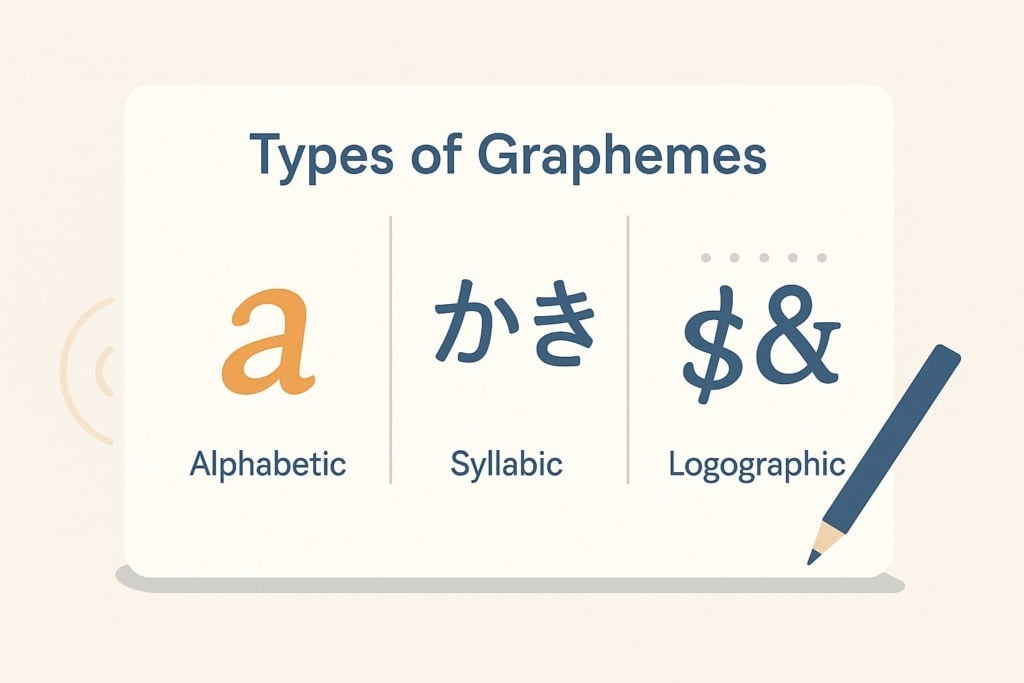
Types of Graphemes
Graphemes can be classified according to the type of writing system:
1. Alphabetic Graphemes
Alphabetic graphemes represent individual sounds (phonemes) and make up the letters of an alphabet.
Examples in English:
- Single letters: b, d, f
- Letter combinations representing a single sound: th in think, sh in ship
Note: English often has irregular grapheme–phoneme correspondences. For example, ough sounds different in though, through, and cough.
2. Syllabic Graphemes
Syllabic graphemes represent entire syllables.
Examples:
- Japanese kana: か (ka), き (ki)
- Some Native American languages use syllabaries to transcribe complex consonant–vowel combinations in one symbol
Note: Syllabic systems are uncommon in English, but the concept remains relevant for comparative linguistics.
3. Logographic Graphemes
Logographic graphemes represent whole words or concepts, rather than sounds.
Examples:
- Chinese ideograms: 山 (mountain), 水 (water)
- Universal symbols: & (ampersand), @ (at sign)
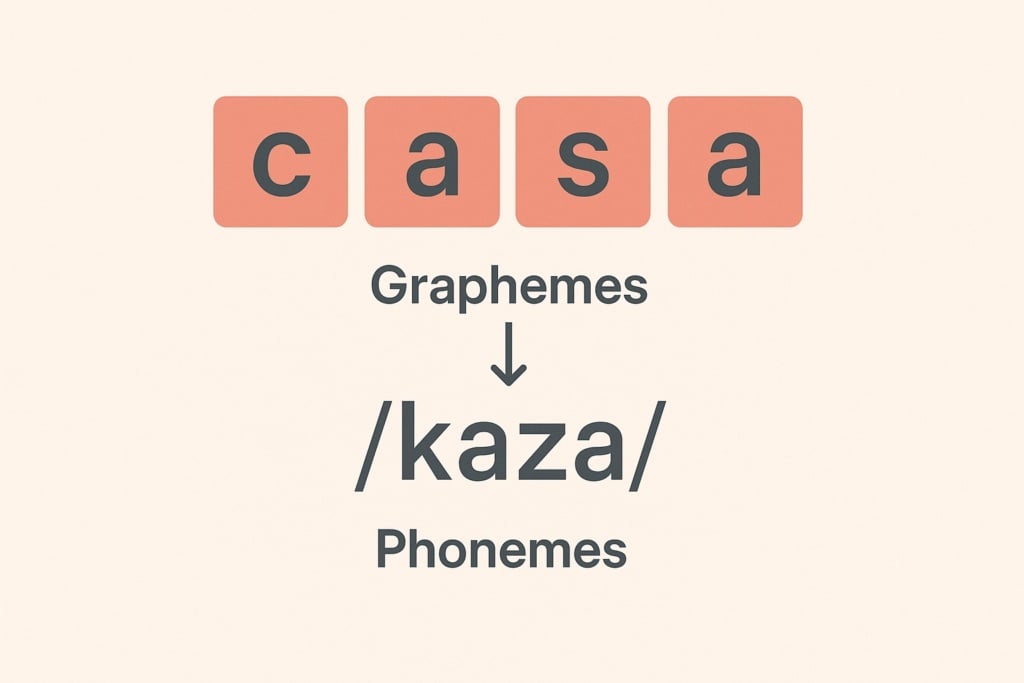
Grapheme vs Phoneme
It is crucial to distinguish between grapheme and phoneme:
| Element | Definition | Example |
| Grapheme | The smallest unit of written language | c in cat |
| Phoneme | The smallest unit of spoken language (sound) | /k/ in cat |
Explanation:
- The grapheme is the written form.
- The phoneme is the spoken sound.
Practical example:
The word ship contains 3 graphemes (s, h, i, p) and 3 phonemes (/ʃ/, /ɪ/, /p/). Note that sh represents a single phoneme /ʃ/.
Grapheme vs Allograph
An allograph is a visual variant of a grapheme.
Examples:
- Uppercase vs lowercase letters: A / a
- Italic vs print: a / a
- Different typefaces: a in Arial vs a in Times New Roman
Explanation:
The allograph changes only the appearance of the grapheme, not its linguistic value.
Practical Examples of Graphemes in English
- Single letters: b, d, m
- Letter combinations: th, sh, ch
- Diacritical marks: café, naïve
- Special symbols: &, %, @

FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a grapheme and an allograph?
A grapheme is the abstract minimal unit of writing, while an allograph is its concrete visual representation (e.g., uppercase, lowercase, italic).
2. What is an alphabetic grapheme?
A grapheme representing a single phoneme within an alphabet. Example: b in bat.
3. What is a syllabic grapheme?
A grapheme representing an entire syllable, such as Japanese kana か (ka), き (ki).
4. What is a logographic grapheme?
A grapheme representing a complete word or concept, such as Chinese ideograms or universal symbols like &.
5. Why is studying graphemes important?
It helps understand the relationship between writing and spoken language, improves reading and writing accuracy, and facilitates the analysis of complex writing systems.
Conclusion
The grapheme is the fundamental unit of written language. Studying graphemes allows us to understand how spoken language is translated into writing, how different writing systems function, and how each symbol conveys meaning.
Understanding graphemes, their types, allographs, and differences with phonemes is essential for:
- Analysing and understanding written language
- Improving reading and writing skills
- Studying complex linguistic systems such as alphabets, syllabaries, and logograms
This guide provides a reference for students, linguists, teachers, and writing enthusiasts.

