Table of Contents
UX Design (User Experience Design) is a discipline focused on creating optimal user experiences in products, services, and systems. The main goal of this practice is to improve user satisfaction and loyalty by creating interactions that are not only pleasant but also simple and functional.
In this article, we will explore what UX Design is, its evolution over time, the differences between UX and UI Design, the design process, the most commonly used tools, and how to apply it to achieve concrete results in the digital world.
What is UX Design?
UX Design focuses on the overall experience that a user has when interacting with a product, service, or system. It’s not just about aesthetics, but also about usability, navigability, and the enjoyment a user experiences. Good UX design should be fluid, intuitive, and satisfying.
The term UX Design was coined in the 1990s by Don Norman, who worked for Apple. His vision was to create more intuitive and user-friendly experiences by placing the user at the center of the design process.
Over the years, UX design has become a key aspect of digital design, as companies have realized the importance of providing an optimal user experience to improve user retention, conversions, and brand perception.

The History and Evolution of UX Design
The concept of user experience has existed for decades, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that it was formalized as UX Design. In the 1980s, the focus was primarily on usability (how easy a product is to use), but in the 1990s, with the introduction of the internet and the first graphical interfaces, there was a need to also focus on user satisfaction.
With the advent of smartphones, mobile operating systems, and apps, UX design has become increasingly crucial, not only for graphical interfaces but for the overall experience, including gestures, tactile feedback, response time, and fluid interaction.
A classic example of modern UX Design application is the iPod by Apple. In 2001, Apple launched the iPod, a music player that revolutionized the market not just for its technology but especially for its user experience. The design of the iPod, with its clickwheel, provided an extremely intuitive interface that allowed users to navigate through hundreds of songs with a single finger. This example is one of the first to demonstrate how a user-centered design can go far beyond aesthetics, aiming to simplify interactions and enrich the overall experience.
Don Norman, who helped define the concept of UX Design, played a key role in designing interfaces like the one in the iPod, where every element was designed to be functional and intuitive, making the user experience smooth and enjoyable.
Difference Between UX Design and UI Design
UX Design and UI Design are often confused, but in reality, they are two complementary but distinct aspects of the design process:
- UX Design refers to the overall user experience, how the user feels and interacts with the product, considering emotions, ease of use, and their needs.
- UI Design (User Interface Design), on the other hand, focuses specifically on the visual and functional aspects of the interface: how buttons, menus, colors, and fonts are organized and how the user interacts with these elements.
In summary, UX Design is the overall experience, while UI Design is the form and function of the interface that the user sees and interacts with.
Why is UX Design Important?
Investing in good UX Design brings numerous benefits, especially for companies operating in a competitive digital environment. Here are some reasons why UX Design is fundamental:
- Improvement in conversions: A carefully designed interface naturally guides the user toward the desired action, such as purchasing, signing up, or completing a form, increasing conversions.
- User retention: A positive and smooth experience makes the user more likely to return, improving retention. An interface that doesn’t create frustration enhances satisfaction and increases the likelihood of the user coming back.
- Reduction in long-term costs: Solving usability problems early in the design phase reduces costs associated with post-launch support and later modifications. Preventing usability issues during the design phase helps avoid losing users and revenue.

How Does the UX Design Process Work?
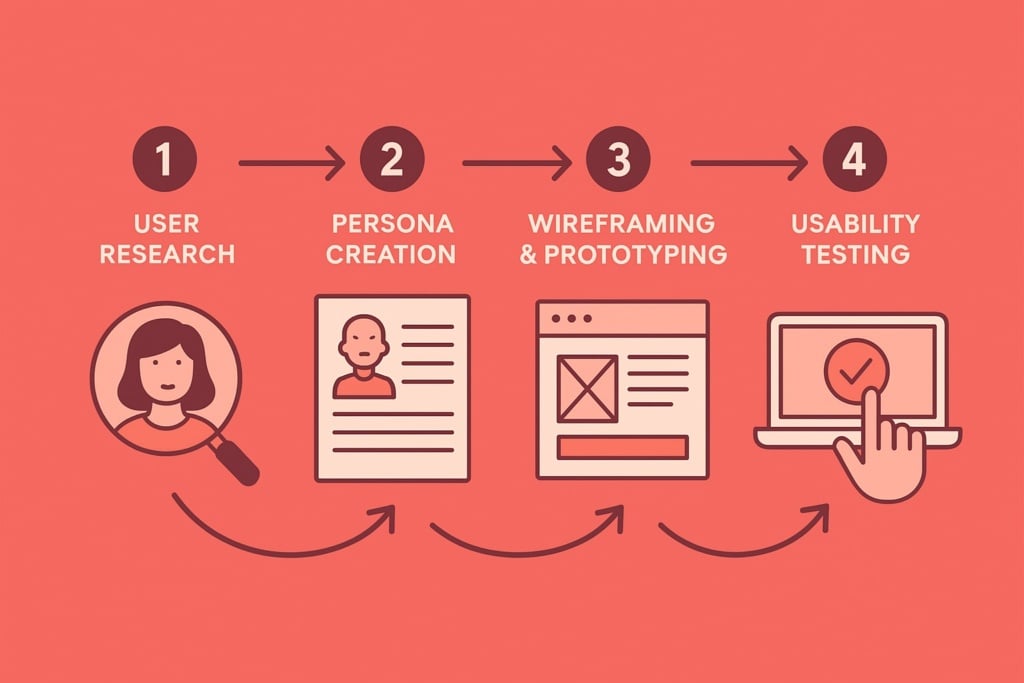
The UX Design process is user-centered and involves several phases. Here’s a breakdown of each phase:
- User research: This phase involves gathering data on how users interact with the product. Research techniques include interviews, surveys, focus groups, and direct observation. The goal is to understand users’ needs, desires, problems, and behaviors.
- Persona creation: Based on the data collected during the research phase, designers create personas, fictional profiles representing key user groups. These personas help designers focus on real users and make more informed decisions.
- Wireframes and prototypes: Once all necessary information is gathered, the design team creates wireframes (interface sketches) and interactive prototypes that demonstrate how the product will function. These prototypes can be tested and refined before final production.
- Usability testing: Before launching the product, it’s essential to test it with real users. Usability tests are conducted to observe how users interact with the prototype and identify any difficulties or problems.
Most Commonly Used UX Design Tools
There are several tools that help designers create and refine their interfaces. Some of the most commonly used include:
- Figma: A collaborative design tool that allows multiple designers to work together in real-time.
- Sketch: Used for interface design, prototyping, and managing reusable symbols.
- Adobe XD: Another powerful tool that allows designers to create interfaces, build prototypes, and test designs.
Why is UX Design Strategic for Businesses?
UX Design is a fundamental business strategy. Companies that invest in UX Design improve their products, reduce operational costs, and increase customer satisfaction. For example, Amazon has built a significant part of its success on continuously improving the user experience, ensuring that customers can easily find what they’re looking for and complete purchases quickly and easily.

Conclusion
UX Design is not a passing trend but a critical discipline for the success of a digital product. Understanding and applying the principles of UX Design means creating user experiences that are not only functional but also exciting and engaging. Investing in the continuous improvement of user experience can lead to tremendous benefits in customer satisfaction, conversions, and brand trust.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About UX Design
What is the first thing I should consider when starting to design the user experience of a product?
When starting to design the user experience, the first thing to consider is understanding who your users are and what their needs are. Conducting user research is crucial to understand their behaviors, expectations, and challenges. Only after gathering this information can you design an interface that truly meets their needs.
How can I ensure that my digital product is easy to use and accessible to everyone?
To make your product easy to use and accessible, you must follow key guidelines:
- Simplify the interaction: minimize the steps required to complete an action, such as making a purchase or signing up.
- Usability testing: ensure that users can easily navigate by testing the design with real people.
- Accessibility: make sure the product is usable by everyone, including people with disabilities, by using tools like color contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen readers.
How do I know if the user experience of my product is effective?
To know if your product’s user experience is effective, you need to gather continuous feedback. Here’s how:
- Analytics: monitor user actions, such as time spent on a page or bounce rates.
- Usability testing: observe how users interact with the product in real scenarios.
- Surveys and reviews: ask users directly how they feel during the interaction and what improvements they would suggest.
What’s the difference between a good user experience and a bad one? Can you give a concrete example?
A good user experience is smooth, seamless, and leads to a sense of satisfaction. For example, when a user uses an app and easily finds what they’re looking for without frustration, it’s a sign of good UX Design.
On the other hand, a bad user experience can result from confusing navigation, overly complex actions, or an interface that doesn’t respond well, creating frustration. For example, on an e-commerce platform, if a user can’t easily find their shopping cart or doesn’t understand how to checkout, that would be a bad user experience.
What are the most common mistakes made when designing a user experience?
Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Ignoring user research: designing a product without truly understanding who the users are and what they want.
- Not testing the design: launching a product without conducting usability tests with the target audience.
- Visual overload: cluttering the interface with too many elements that distract the user rather than simplifying the interaction.
- Not optimizing for mobile devices: neglecting the user experience on mobile devices, especially since most people today access digital services via smartphones.
When is it necessary to update or rethink the user experience design of a product?
It’s necessary to update or rethink the user experience design when:
- Users are abandoning the product: if many users abandon the product without completing the desired actions, there could be a usability issue.
- Negative feedback: if you receive a lot of negative feedback about usability or if users feel frustrated, it’s a sign that something in the design isn’t working.
- Market evolution: when new devices or platforms become popular, it may be necessary to rethink the design to optimize the experience on new technologies.
How can I integrate UX Design into my business strategy?
To integrate UX Design into your business strategy, you need to prioritize user experience at every stage of the design, development, and marketing processes:
- Create a user-centered culture: all team members, from marketing to design, must share the goal of creating an optimal user experience.
- Constantly monitor: use analytics and feedback to monitor and continuously improve the user experience, adapting it to evolving user needs.
- Invest in research and testing: even after the product is launched, keep testing and gathering feedback to optimize the experience.
What are the main benefits for a company that invests in UX Design?
Investing in UX Design offers numerous benefits:
- Increased conversions: a smooth and intuitive user experience makes it easier for users to complete desired actions, such as making purchases and signing up.
- Customer loyalty: an experience that meets users’ needs leads to retention and long-term relationships.
- Brand reputation: good UX Design contributes to a positive perception of the brand, fostering word-of-mouth and improving market position.