Table of Contents
We’ve discussed the customer journey a lot on this blog over the years. We’ve pondered what it means and how best to map it and we’ve developed some handy guidelines for categorising and managing it.
The topic is close to our hearts for two main reasons. Firstly because it’s an essential part of optimising your marketing and developing your business. And secondly because of the amount of research that continues to be conducted on the subject, tracing its evolution over time.
A brief history of customer journey research
Here are some key milestones in research in this area:
- Several decades ago, researchers came up with the first funnel models, including AIDA (an acronym of the four main stages of the user journey: Attention/Interest/Desire/Action). This later became AIDAR, with the addition of a final stage: Retention.
- From 2009, the focus shifted to this ‘new’ retention phase and to the idea of the ‘loyalty loop’, with the global consulting firm McKinsey’s studies into the consumer decision journey playing a key role.
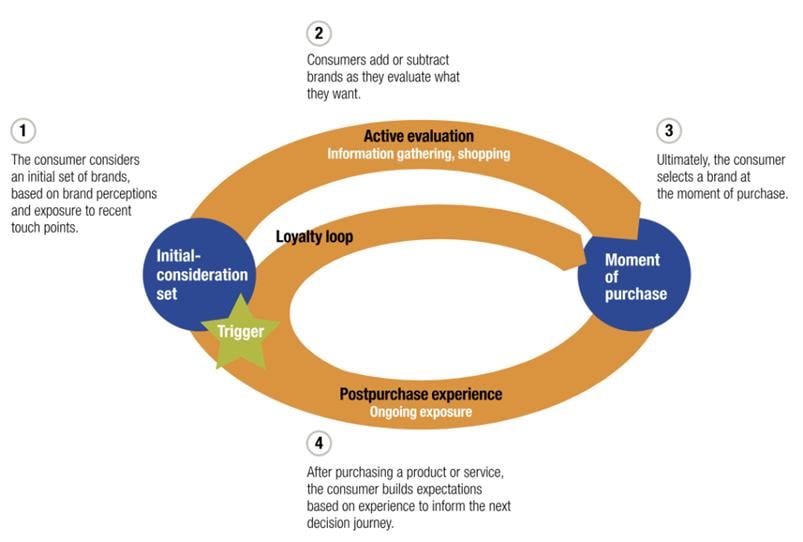
- In 2020, Google introduced the concept of the messy middle to describe the chaotic, non-linear decision-making process between the time a consumer’s need arises and them making their purchase. The messy middle involves a continuous cycle of exploration (searching for options) and evaluation (product analysis), during which consumers are influenced by a wealth of information, reviews and their own cognitive bias.
- Most recently, another global consultancy firm, BCG, proposed a new digitally focused customer journey, which states that there are four key behaviours underpinning today’s consumer experience that are reshaping the way people discover and interact with brands: streaming, scrolling, searching and shopping.
However, in recent months, the arrival and rapid spread of Generative AI in searching for content, information and answers has created another paradigm shift. We are now moving from a context dominated by pages of results to one based on summaries generated by Large Language Models (LLMs) that pull together a range of different content, often including citations and sources.
Generative AI in people’s searches
‘Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence that can create original content, such as natural language, images, audio, and code. The output of a generative AI is based on the inputs provided by the user. One common way for users to interact with generative AI is through chat applications that use natural language as their input. ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is a popular example of this. Generative AI applications that use natural language as an input are powered by large language models (LLMs) to perform natural language processing (NLP).’
This quote from Microsoft provides a good starting point for understanding generative AI and LLMs – the most famous of which is undoubtedly ChatGPT. According to recent research, ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini are the two LLMs users are most familiar with. People have even started treating the former like a friend, affectionately calling it ‘Chat’.
In September 2025, ChatGPT – or rather its developer OpenAI – released an interesting study, How People are Using ChatGPT, based on analysis of how users like us are taking advantage of the tool.
The results are interesting:
- Three-quarters of conversations with the AI chatbot are focused on practical information, searching for information, or writing, with writing the most common work activity. Programming and self-expression remain more niche activities.
- 70% of the conversations we have with ChatGPT are for personal use, while 30% are for work-related purposes.
- The use cases can also be divided up into three large families: asking, doing and expressing. Roughly half of prompts (49%) are linked to asking, showing that people prefer to use ChatGPT as an advisor rather than for completing an entire task. Doing (40% of all prompts, including approximately one-third of work use) includes interaction linked to tasks like drafting text, planning or programming, where the model is used to generate outputs or complete practical work. Expressing (11% of total usage) incorporates all uses that are neither asking nor doing, and which usually involve personal reflections, exploration and play.
The spread of AI Search
Basically, we are increasingly using artificial intelligence to ask questions. But what effect is this having on the customer journey?
Spoiler: the effect it is having is large, wide-ranging and still growing! An article published by Bain maps the most common prompts we use in our interactions with ChatGPT: asking the machine for shopping tips is now commonplace, as is demanding that it analyses and interprets diagnoses and tests relating to our health and psychological and physical wellbeing (indeed, AI chatbots are increasingly being used in place of psychologists).
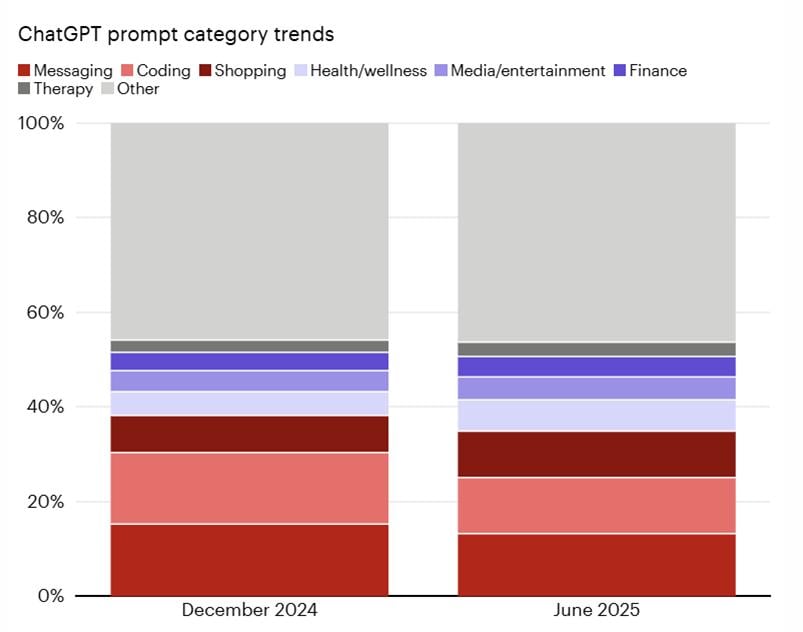
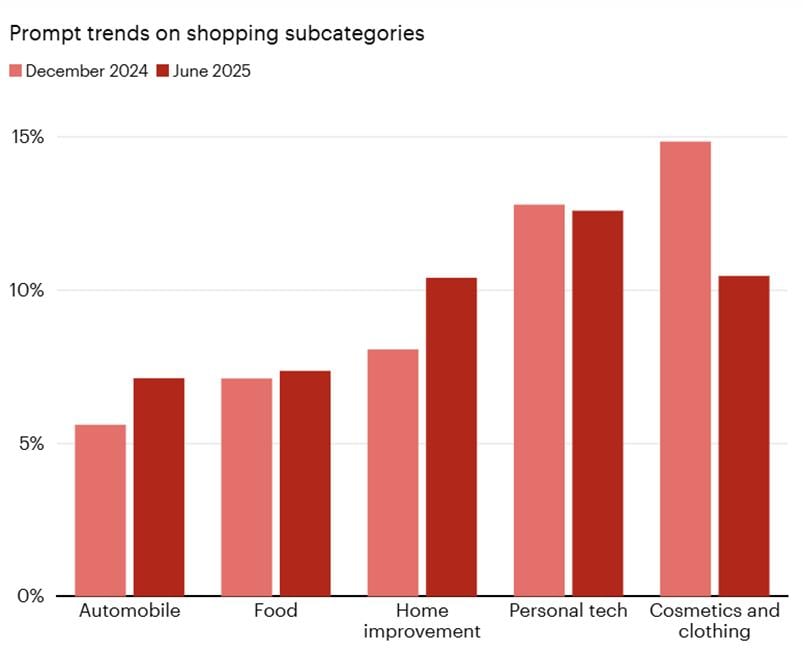
When you look in more detail at the data on purchasing habits, it becomes clear that some products are gaining ground over others, with the strongest signals coming from tech, DIY, cosmetics and clothing.
There has also been an increase in the number of links added to ChatGPT’s replies: click-throughs tripled between March and June 2025, from 100,000 to 300,000!
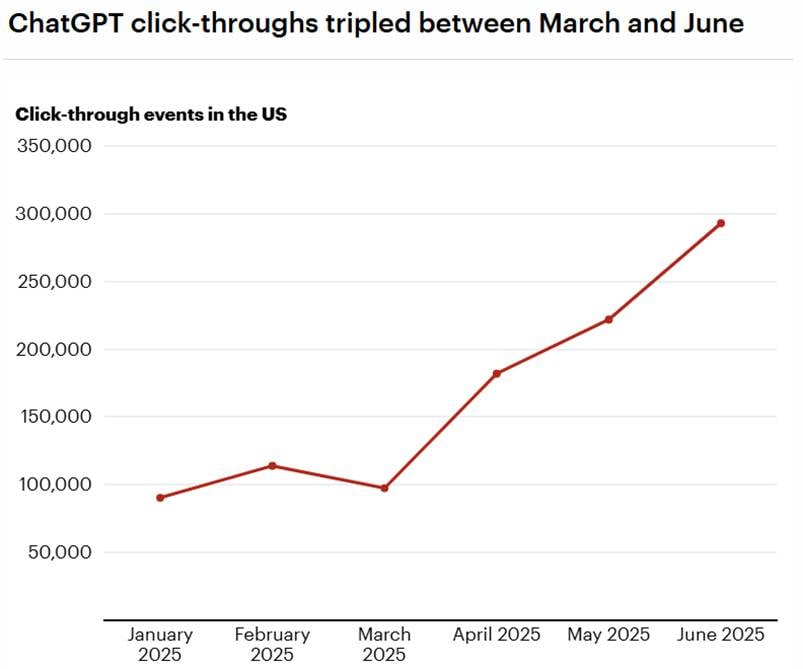
This change suggests that users are not solely using ChatGPT for advice, but also to find links to products or specific content similarly to how they might use a traditional search engine.
The advent of generative AI has also had a major impact on how we consume content when conducting traditional searches on search engines. In spring 2024, Google introduced the AI Overview – an AI-based evolution of the snippet (the box at the top of the search page showing an extract from the most relevant result). This function uses AI to generate an automatic summary that provides an instant response to questions of varying levels of complexity. Here, for example is the AI Overview explaining… the concept of the AI Overview 😋:
The AI Overview was quickly followed by AI Mode, designed for more complicated search situations and dynamics. Clicking a button on the Google bar inside the search engine completely changes the search experience. Instead of simply showing results, it analyses and summarises information from various sources before providing a single answer, including processing complex questions and enabling conversational interactions (for example through images or voice).
Links are no longer at the heart of the search; they are more of an appendix used to show where the information displayed in AI Mode came from.
AI Overview and AI Mode can be defined as AI summaries – AI-generated results provided by Google to optimise people’s searches and their customer journey.
But what tangible effects is this having? Research conducted by the Pew Research Center, which analysed how 900 American adults searched for content and information in March 2025, produced some interesting results:
- Google users who encounter AI summaries are less likely to click links to other websites than users who don’t. They often don’t even click on any links found in the summary itself! Indeed, during his presentation of the AI Mode feature, Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai described it as an ‘end-to-end AI Search experience’. You don’t get much clearer than that!
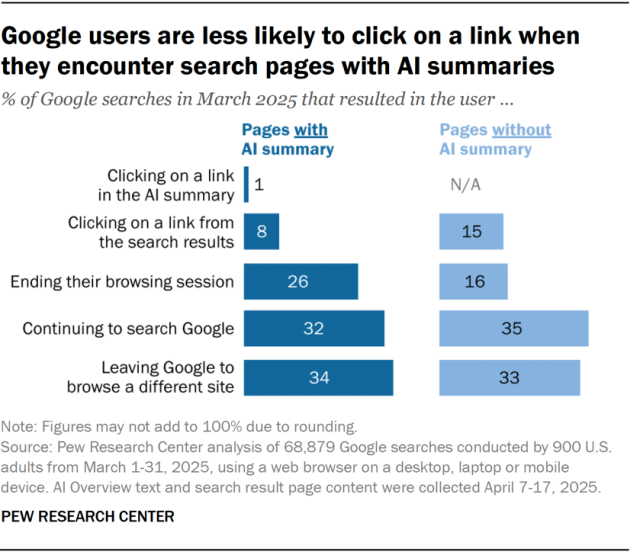
- Users are more likely to completely stop their browsing session immediately after visiting a search page with an AI summary than if they visit pages without them.
- The most frequently cited sources in both Google summaries and standard search results are Wikipedia, YouTube and Reddit.
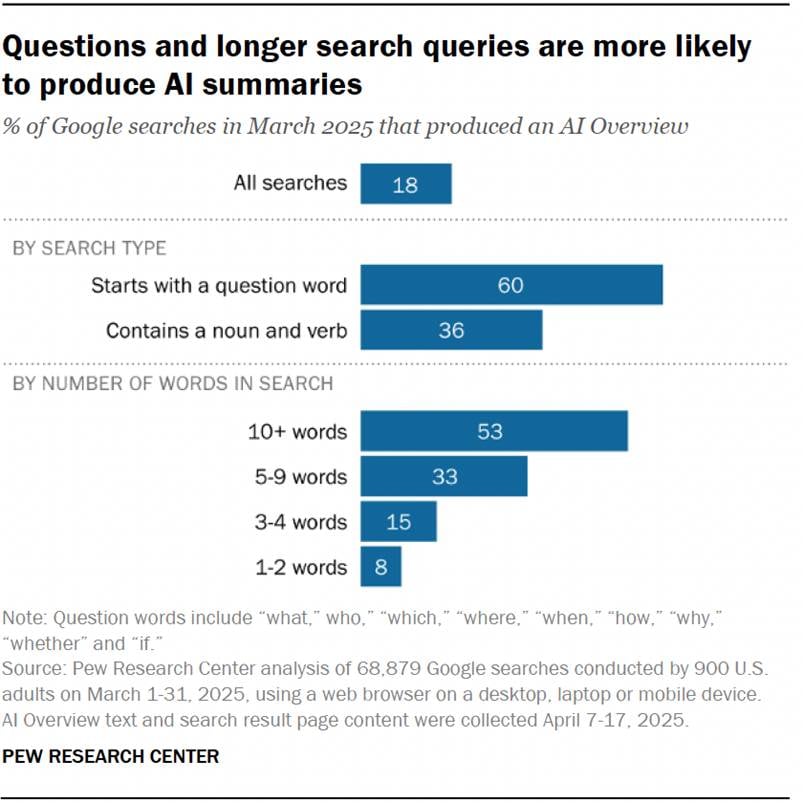
- Google searches that contain multiple words, ask questions or use complete sentences tend to produce AI summaries more frequently.
How online content and channels are evolving in the era of conversational AI
I hope there is one message in particular you will take away from this article: AI is here to stay, and it’s having a major impact on all customer journeys, including your own customers. But what can you start doing to make sure you’re prepared?
If you run a content-based website or an e-commerce business, you need to be aware that it is no longer enough to be mentioned through (traditional) SEO strategies: artificial intelligence optimisation (AIO), also known as generative engine optimisation (GEO), means you need to be linked to, and appear in, the LLMs’ replies too.
A BBC article imagined a dystopian scenario where these new AI chatbots and LLMs caused a dramatic fall in visits to web pages, and discussed the concept of the machine web: an internet where websites are designed to be read exclusively by machines, and where the only way to get information is through the summaries and rehashing provided by AI. In other words: machines are becoming the audience.
That said, it is worth highlighting that generative AI has not (yet?) replaced traditional search methods, both due to habit, and to the mistrust that still hovers around AI-optimised user searches. So, for the time being at least, you need to consider conversational AI as yet another channel through which people can find content and information, and therefore businesses and brands.

